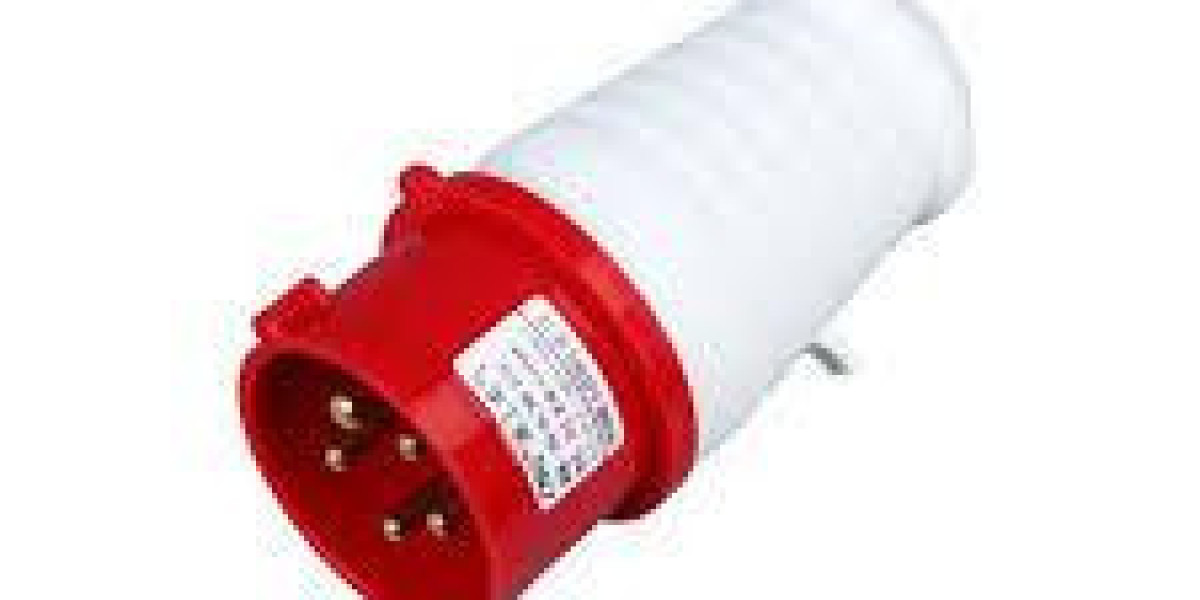
Critical infrastructure depends on dependable connectors — in demanding plants and field sites the Industrial Plug must deliver secure contact under load, and early specification of the correct Industrial Plug reduces mismatch, simplifies maintenance, and increases uptime. Thoughtful selection, correct installation, and routine servicing form a lifecycle approach that keeps personnel safe and equipment running.
Standards, ratings, and specification basics
Begin by documenting the electrical characteristics and environmental stresses the connector will face. Specify voltage, continuous current, fault-current withstand, and whether single- or three-phase service is required. Match these needs to recognized standards—IEC, UL, or local equivalents—so the device’s ratings are traceable. Ingress protection (IP) or NEMA classifications should reflect site realities: washdown operations, temporary immersion, or heavy dust require progressively higher protection. Request factory test reports and material certificates during procurement to validate claimed performance.
Contact metallurgy and mechanical design
The heart of any connector is the contact system. Choose contact materials and platings that combine conductivity with corrosion resistance; silver- or nickel-plated copper alloys are common because they preserve low resistance while resisting oxidation. Contacts with deep engagement and secure retention reduce the chance of arcing during mating cycles. Mechanical design choices—whether threaded, bayonet, or cam-lock coupling—affect vibration resistance and ease of use. Reinforced housings and captive fasteners reduce maintenance errors and the risk of lost parts in the field.
Environmental sealing and ingress protection
Sealing is a system issue: glands, gaskets, and mating interfaces must all be rated to the same protection level. Use cable glands that carry the same IP rating as the connectors and ensure glands are correctly torqued to maintain compression. In corrosive or coastal environments, select materials and coatings that resist salt spray and chemical attack. For high-hygiene or washdown areas, hygienic designs and compatible seals prevent contamination while allowing routine cleaning with aggressive detergents.
Installation best practices and cable management
Correct installation extends connector life. Terminate conductors with recommended lug sizes and use torque-controlled tools to avoid loose or over-compressed joints. Route cables with proper bend radii and secure them with suitable strain reliefs so mechanical loads do not transfer to the termination point. Mark phases and maintain clear wiring diagrams accessible at the connection panel to aid future troubleshooting. When mounting panel sockets, ensure flange seals remain compressed uniformly and avoid using incompatible fasteners that could introduce galvanic corrosion.
Testing, commissioning, and verification
A thorough commissioning sequence confirms the installation’s robustness. Insulation resistance and continuity tests verify correct wiring and detect damaged insulation. Measure contact resistance on power terminations to identify high-resistance joints before they heat under load. For significant power circuits, conduct thermal imaging under representative load to reveal hotspots. Record test results, torque values, and serial numbers in the commissioning dossier for traceability and future diagnostics.
Maintenance program and spares strategy
Establish a maintenance cadence based on environment and duty cycle. Frequent inspections are critical in aggressive atmospheres—look for seal degradation, contact discoloration, or signs of moisture ingress. Replace gaskets and O-rings before failure and keep critical spares on hand: contact inserts, gland seals, and common-sized locking rings. For intermittent faults, use a known-good mating assembly to isolate whether the issue is in the plug, socket, cable, or downstream equipment. A compact spare kit and response plan reduce mean time to repair.
Safety features and accessories
Value-added features improve safety and reduce human error. Keyed inserts prevent mismating of different voltages or phases, while interlocks stop live mating when a cover is open. Dust caps protect unused sockets, and color coding simplifies identification. For sensitive electronics, include EMI/RFI shielding or surge protection modules. Pre-wired cable assemblies and factory-terminated leads minimize field labor and the chance of termination errors.
Procurement checklist and lifecycle considerations
When procuring connectors, require detailed datasheets, IP/NEMA ratings, and independent test evidence. Specify expected fault-level performance and coupling mechanisms suitable for expected mechanical stresses. Evaluate supplier quality systems and their ability to provide spares and technical support. Factor in lifecycle costs: a slightly higher initial investment in robust connectors, tested assemblies, and spare inventories often yields lower total cost through reduced failures and downtime.
Thoughtful specification, correct installation, and a predictable maintenance program together ensure that power connections remain safe and reliable across industrial sites. For a practical, manufacturer-focused technical overview and guidance on industrial plug applications, visit https://www.nante.com/news/industry-news/what-is-industrial-plug.html