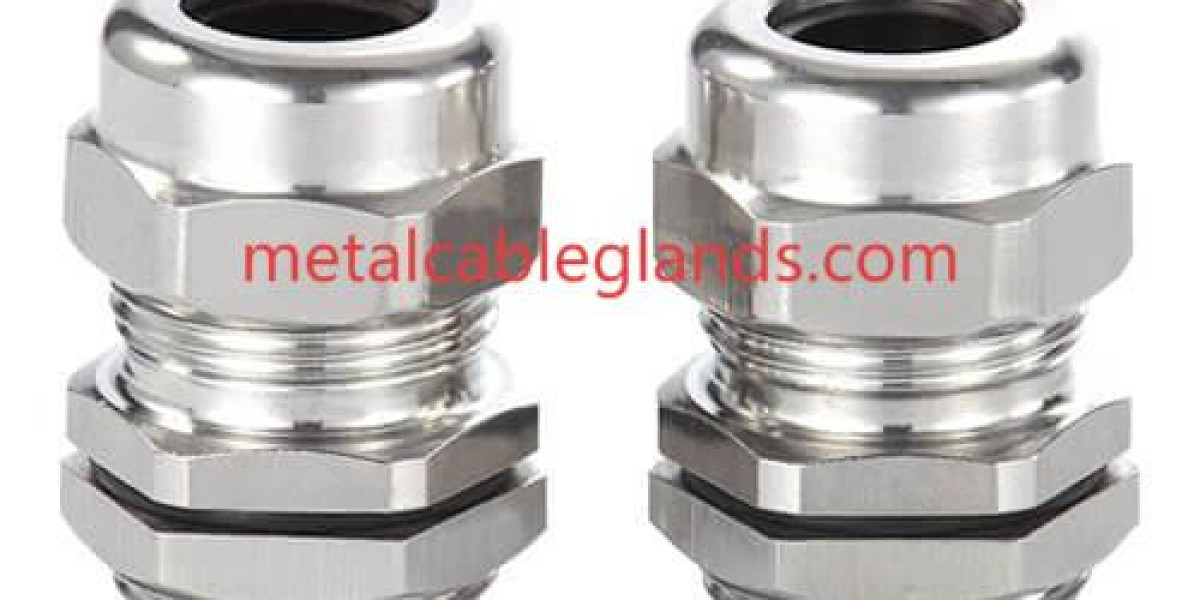
In complex electrical installations, system designers often refer to EMC Cable Gland solutions mid-sentence when evaluating how to maintain electromagnetic stability without increasing enclosure complexity. These components are valued not only for their physical role in cable entry but also for the functional integration they provide within shielding and grounding strategies across modern electrical systems.
At the functional level, EMC cable glands are designed to act as controlled interfaces between shielded cables and enclosures. Their internal structures are shaped to create stable contact with the cable’s shielding layer, allowing electromagnetic disturbances to be guided away from internal circuits. This functional interaction transforms the cable entry point from a potential vulnerability into an active contributor to electromagnetic control.
Performance consistency is one of the defining characteristics of EMC cable gland systems. During installation, cables may be adjusted, repositioned, or replaced, yet the gland must continue to maintain effective contact with shielding layers. This requirement places emphasis on internal gripping mechanisms that adapt to movement without degrading electrical continuity. The ability to sustain this contact supports long-term operational reliability in dynamic environments.
Another important functional aspect is how EMC cable glands support enclosure integrity while managing electromagnetic behavior. Cable entry points often represent interruptions in enclosure shielding. By integrating conductive paths within the gland body, EMC designs help bridge this interruption, allowing shielding effectiveness to extend through the entry point. This integrated approach reduces the risk of electromagnetic leakage where cables pass through enclosure walls.
In control and automation systems, EMC cable glands play a crucial role in maintaining stable communication and control signals. Equipment such as controllers, sensors, and interface modules operate within tightly managed electromagnetic environments. The functional contribution of EMC cable glands helps minimize signal disruption caused by external noise or internal equipment interaction, supporting predictable system behavior during continuous operation.
Performance demands are particularly evident in environments where power and data cables coexist. Without effective control, electromagnetic interaction between these cable types can compromise system efficiency. EMC cable glands help manage this interaction by reinforcing shielding continuity at the entry point, supporting cleaner signal transmission and reducing the likelihood of interference-related disruptions.
In manufacturing facilities, where equipment cycles frequently and electrical systems are exposed to constant operational stress, EMC cable glands contribute to performance resilience. Their ability to maintain functional stability over repeated use aligns with the demands of high-duty applications. This reliability supports maintenance efficiency by reducing the need for frequent adjustments or corrective actions related to electromagnetic issues.
Transportation and infrastructure projects also place unique functional demands on EMC cable glands. Systems used in signaling, monitoring, and control often operate in environments influenced by external electromagnetic sources. EMC cable glands help isolate internal electronics from these influences, supporting stable operation even when environmental conditions fluctuate.
The effectiveness of these functions depends heavily on production quality and design discipline. Zhejiang Hongjuesi Connector applies structured manufacturing practices to ensure that EMC cable glands deliver consistent functional behavior. Attention to internal geometry and conductive continuity supports reliable performance across varied installation scenarios.
As electrical systems continue to evolve toward higher integration and increased data exchange, EMC Cable Gland applications remain essential for maintaining balanced electromagnetic conditions. For engineers and project planners seeking EMC-focused cable entry solutions that align with functional performance expectations, further product information can be found at https://www.metalcableglands.com/product .